Podcast: Download
Subscribe: Apple Podcasts | RSS
 Ever since my TEDx Talk cracked several million views, people from around the world have asked me how to memorize a presentation.
Ever since my TEDx Talk cracked several million views, people from around the world have asked me how to memorize a presentation.
Beyond that presentation from the stage, what qualifies me to offer you tips for memorizing a speech of any length?
Well, I also spent a decade as a professor at three universities in three different countries. I delivered dozens of lectures during those years. In more than one language.
I’ve also spent over a decade as an online “professor of memory.” My expertise in memory has taken me around the world. I’ve given presentations in Germany, Switzerland, Austria, England, China, Canada, Australia and the USA.
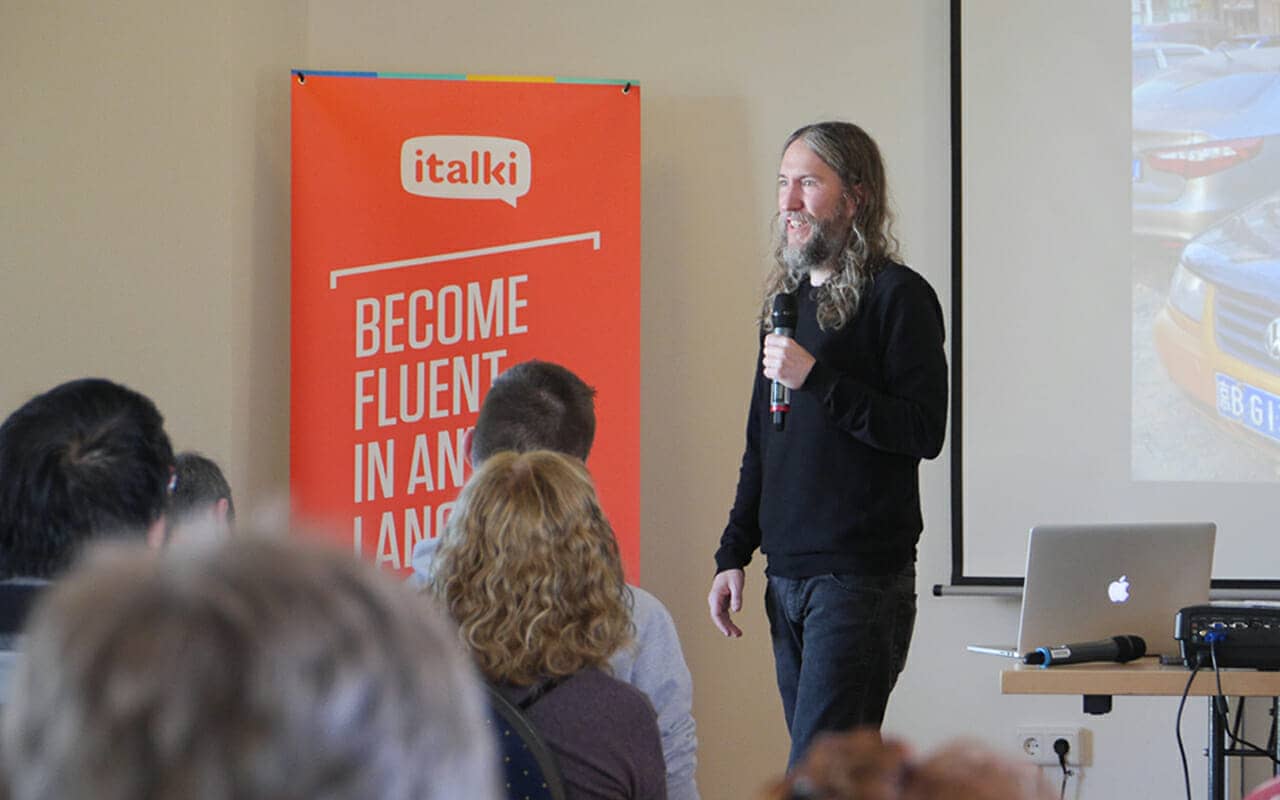
In fact, in the feature image for this post, you see me discussing memory as a part of language learning at a 2016 Polyglot Conference in Berlin. You can also watch hundreds of hours of my presentations on YouTube from several years of live streaming.
And on this page, I’m going to share the best of my experiences with multiple kinds of presentation.
If you want to memorize a speech verbatim, I’ll show you how.
Or, if you prefer to work from mental bullet points, I’ll help you do that too.
When it comes to memory aids for speakers, this is the real deal from someone who practices these techniques week in and week out.
Ready?
Let’s get started!
So You Need to Memorize a Presentation… Here’s Where to Start
Getting started… this is the tricky bit.
So here’s a story using the Polyglot conference speech I gave to help dimensionalize the starting point I usually use.
Determine Who Your Presentation Is For… And Who It Isn’t For
Before I wrote a single word, I asked myself a very simple set of questions:
Who can I help and who am I unable to help?
And what’s the one thing that will help the listeners above all?
I went through this same process with my TEDx Talk and many other presentations.
Make no mistake, this step can be tricky. It’s a discipline to whittle things down to the biggest and most important point.
But it is possible and often the success of the talks we enjoy most come down to knowing that the audience you’re addressing is defined as closely as possible.
It was hard for me, but I believe focusing on just one kind of person and one message for that person helped my TEDx Talk reach so many viewers.
Of course, some presentations need more details and more nuance, but even then, the principle is the same. If you think about who each principle is for and how to focus on the biggest and most impactful part, it’s going to be easier to digest. And easier for you to remember successfully.
Script The Presentation
When it comes to helping yourself remember your presentation, writing is key. If you write a bunch of mush with endless long sentences, you’re setting yourself up for a struggle.
So when you’re putting the presentation together, ask yourself:
- Do I want to memorize the speech verbatim?
- Or can I memorize keywords and let my expertise fill in the blanks while speaking?
Both ways work very well. It just comes down to your goal. In the case of my TEDx Talk, I wrote the speech and memorized it verbatim.
In my Polyglot Conference talk, I prepared slides and memorized the key points, which involved speaking some Chinese based on how I’ve studied that language.
Either way, scripting or preparing slides can help you decide how you’re going to memorize the presentation.
Review The Presentation
As a final preparation step, it’s great if you can take a moment to review what you’ve prepared. Ideally, you’ll also get at least one other person to review it as well.
For my TEDx Talk, Thomas Krafft reviewed the script itself and a recording of me delivering it from memory. Before presenting the script of my live-action “Memory Detective” game attached to a memory improvement novel I wrote, I had a test audience go through the entire sequence.
Reviewing the speech, slides and related materials with others helps add an extra layer of understanding that helps with the memorization process. I highly recommend making time for review.
How to Memorize a Presentation from Start to Finish in 7 Easy Steps
As Hanna Pishwa points out in Language and Memory, Aristotle was one of the first to intensively describe the rhetorical strategies used for persuasion in speeches.
But we can go a step further: Aristotle also closed his treatise on memory by explaining that we are moved most by people who speak from memory.

He says reciting from memory is impressive because the person who has memorized their speech doesn’t have to “hunt” for their ideas. They use a “process” that brings those ideas to them automatically.
How can you do that too? Just follow these steps:
One: Learn To Use The Memory Palace Technique
Since long before Aristotle, people have been using the ancient art of memory to commit speeches to memory using Memory Palaces.
A Memory Palace is simply a mental copy of a location you know well, like you home, office, school, church or any place with walls, paths and other environment features.
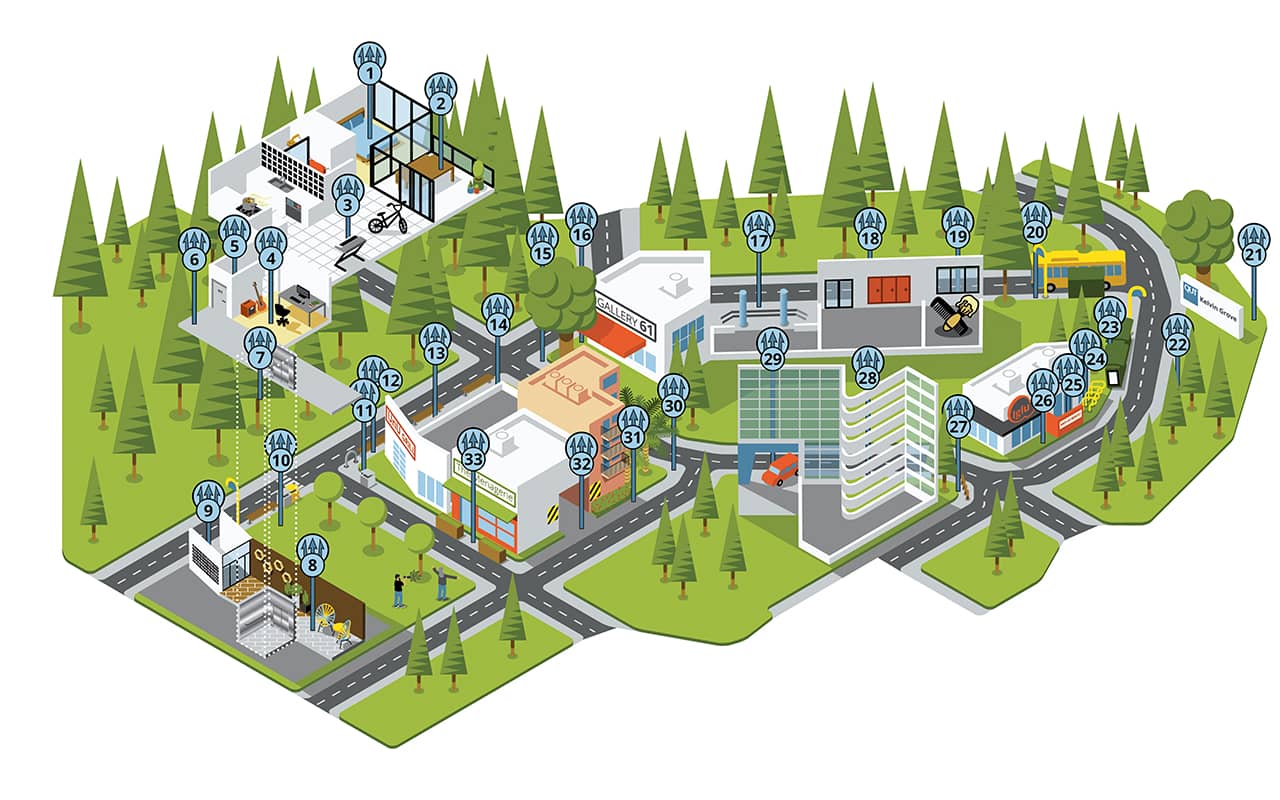
This is a graphic representation of the Memory Palace I used to memorize my TEDx Talk:
It’s a neighborhood in Brisbane and the numbers represent individual stations.
I teach people who take the Magnetic Memory Method Masterclass to number their stations to help them rapidly create these simple journeys.
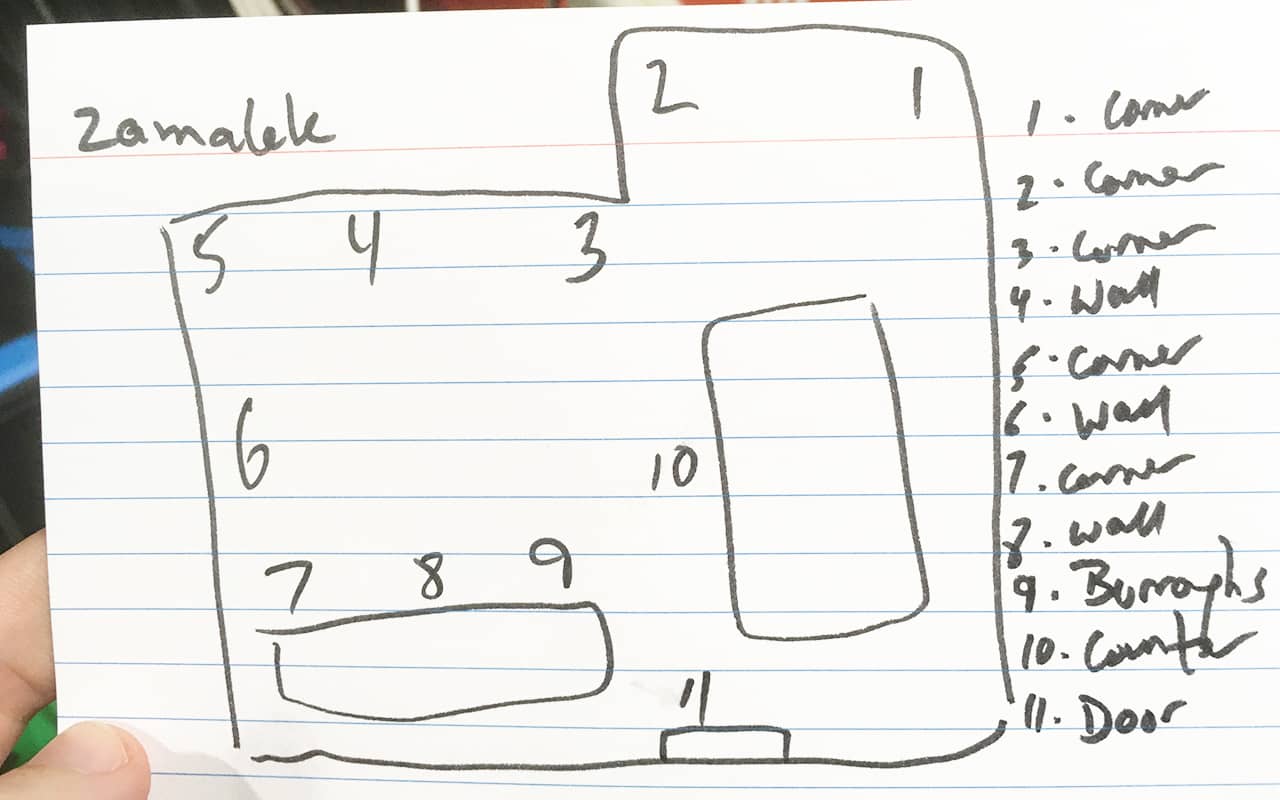
To do this, it’s helpful to draw your Memory Palaces first. Like this:
Two: Add Interesting Associations To The Words & Ideas In Your Presentation
The best memory techniques all rely on mnemonic imagery.
When it comes to how to memorize lines for a presentation, you can do this very quickly by tapping into a pegword list.
For example, in a speech that starts with, “How would you like…?” my pegword list suggests Howie Mandel for “how” and Elijah Wood for “would.”
Those figures are laid out in the Memory Palace at the beginning of its journey.
This leads us to the next step.
Three: Make Your Associations Zany
Let me make a preemptive strike here:
A lot of people have protested to me over the years:
I’m not creative. I can’t get myself to see Howie Mandel and Elijah Wood to kick a like button on a platform like YouTube.
Stop right there.
I’m not creative either.
All I’m doing is taking too people who already exist and having them do something strange. There are only so many actions in the world. They could kiss the like button, put it in a rocket ship and send it to the moon, or bury it with thumbs-up shaped shovels.
Seriously. There’s nothing “creative” about this. It’s just borrowing from real possible actions and animating them in the Memory Palace. Please don’t overthink this process and make sure of the exercises I’m going to share with you in step four.
If you’re memorizing your presentation verbatim, you’ll need more associations than you would for a speech delivered based on bullet-points.
Either way, the process is the same.
Four: Make Your Associations Multisensory
Once you’ve decided what your characters are going to do with one another, add some multisensory elements. For example, you can hear the voices of your celebrity associations, or imagine that you’re feeling them interacting with the like button in our example.
We do this because scientific research makes it clear that elaboration helps form memories faster.
To get better at making your associations weird and multisensory within seconds, these elaborative encoding exercises will help, as will these visualization exercises.
Five: Use The Memory Palace To Memorize Your Speech
When the ancient Romans delivered their speeches, they often would start a persuasive passage with a set of points.
“In the first place,” an orator would say before diving into the point. Then the orator would say, “In the second place,” etc.

This convention in speeches remains with us today, and those orators were literally using their Memory Palaces in real time to recall their points.
But you can be sure that they had practiced in private before delivering them. We know that Rhetorica Ad Herennium, originally attributed to Cicero, gives many suggestions around how best to practice for both public speaking and reciting poetry.
And you need to practice as well.
You do it by starting at the “first place” of the Memory Palace and then triggering those images to help you recall the words.
Personally, I practice my speeches by following several patterns. For example, instead of always starting at the beginning, I will practice reciting a few lines from the end, then switch to the beginning, then go to a spot in the middle.
This is helpful in ushering the speech into long term memory quickly because it harnesses the primacy effect, recency effect and serial-positioning effect.
Six: Practice Delivering The Speech
Now, this point is a subtly that I personally find important.
I do not go through my Memory Palace while delivering my presentations unless I absolutely have to do so.
See, when you follow the process I’ve described above, the presentation will be in your long term memory.
However, unexpected things can happen. During my TEDx Talk, people laughed at a spot I hadn’t placed a joke. It surprised me for a second and I briefly popped into the Memory Palace I’d made to help me get back on track (instead of standing there like a deer caught in headlights).
But ideally, you want to just have the speech memorized and not have to rely on any mnemonic strategies while in the moment. With optimal setup and execution, the memory techniques will have already done their job and you can do what Aristotle described: speak without looking like you’re hunting for the ideas.
And that means you can connect with that audience you identified during the preparation stage. The more you connect with them, the more successful you’ll be during and after your presentation because people remember connection.
Seven: Analyze Your Performance
Want to be a pro speaker?
Then you’ll want to spend some time reflecting on your presentation.
This step is important because it gives you the opportunity to identify areas to improve the next time.
And it will help you congratulate yourself where credit is due. Please make sure to do so. Giving a speech is a huge accomplishment and you deserve recognition merely for making it happen.
But the real gold is some objective and subjective reasoning about the entire process. It will also reveal new ideas for other presentations you might not have thought about otherwise.
In a Pinch? Here’s How to Memorize a Speech Fast
I know that some people don’t have time for all of the steps above.
To be clear: I do all that I can to make sure I have enough time.
But when I don’t, here’s what I do instead.
The Acronym Method
I’m often invited to speak in the community at the last minute. I literally don’t have time to mindmap more than a few ideas.
But I can take those ideas and arrange them into a keyword.
For example, when I was invited to speak at a “Masters of Marketing” event, I arranged my ideas into the acronym F.R.E.E.
- Frequent messaging to a…
- Relevant audience…
- Entertains, Educates and…
- Engages in the direction of a response
I placed that acronym in a simple Memory Palace and talked about what each concept mean for two minutes each.
The great thing about the acronym approach is that you don’t have to practice as much, if at all. The logic of the acronym itself guides you through the parts of your presentation because you’re mentally checking them off by spelling the acronym.
Give this presentation technique a try and you will have no problem committing presentations to memory fast.
Memorize Your Speech in No Time With the Steps Above
Let’s recap:
Presentations are so much easier to remember when you’re clear about who you’re addressing and who you’re not.
Once you’ve decided on whether you’ll be speaking verbatim or working from bullet points, the Memory Palace technique is a tried and true technique with thousands of years of success stories.
To make information “stick,” you need a process of elaborating associations. A bit of prep will take you a long way if you complete the exercises I shared on this page.
Finally, it’s worth repeating that reviewing your talk in any way possible is tremendously valuable. Even if you get a last minute invite to speak, you can probably squeeze in a few minutes to record yourself on your phone and tweak a few things.
Even if you don’t have time to change anything, just seeing yourself once will give you ideas about how to make what you’re about to say in front of an audience better.
Just make sure to avoid perfectionism. Relax and if you make a mistake, just call a spade a spade and find your way back to where you got lost.
And if you want more on the memorization process so you always recover quickly when things happen during live presentations (as they inevitably will), check out my FREE Memory Improvement Kit:
So what do you say?
Are you ready to get out there and give the best presentation of your career?
Let me now if you have any questions and I’ll be happy to share with you more granular details from my long career of presenting around the world.
Related Posts
- How to Memorize Something Fast: 5 Simple And PROVEN Memory Techniques
Wondering how to memorize things fast? Read this post for 5 solid steps you can…
- How to Memorize the Books of The Bible: 7 Easy Steps
Learning how to memorize the books of the bible is easy. You just need these…
- How to Memorize The Quran Fast: 10 Proven Steps
This detailed guide helps you learn how to memorize the Quran. Learn to commit the…